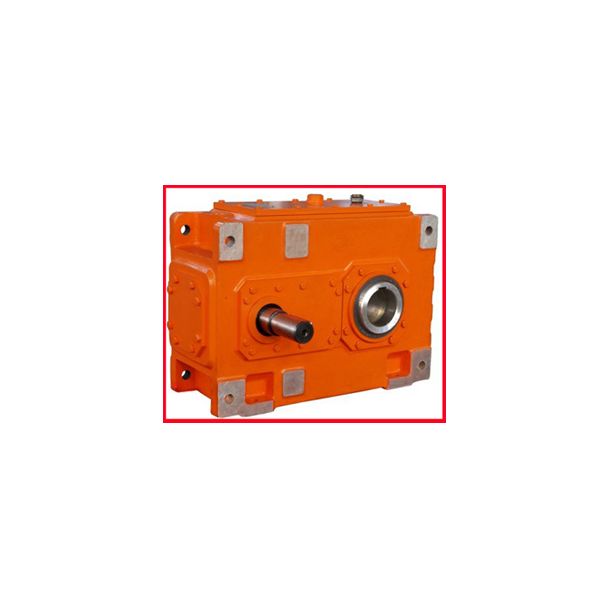
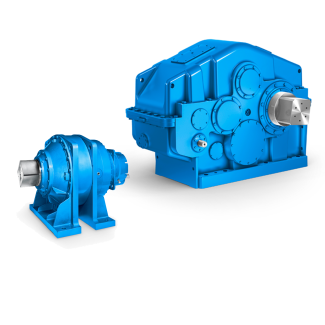
rdering data continued Low speed shaft LSS Oil B3DH-9-C Bevel-helical speed reducer B3
In stock
SKU
B3DH-9-C
$19,285.71
Flender/Flender Gear Units/Bevel-helical speed reducer B3
rated in single layer. nickel lm is deposited in an electroplating process, serving as bond for the diamonds and joining them to the steel body. An alternative to electroplating is sintering where the diamonds are placed or scattered into graphite
them to the steel body. An alternative to electroplating is sintering where the diamonds are placed or scattered into graphite  mould. The cavity between the diamond coating and the body is lled with wear-protective powder containing tungsten, and is sintered
mould. The cavity between the diamond coating and the body is lled with wear-protective powder containing tungsten, and is sintered  at high temperature. Steps must be taken to prevent temperature-induced distortions [ LIER0 ]. Dressing Process The dressing process and
at high temperature. Steps must be taken to prevent temperature-induced distortions [ LIER0 ]. Dressing Process The dressing process and  the resulting grinding wheel structure are dened by: the ratio between the circumferential speeds of the grinding wheel and the dresser roll (dressing ratio) the dressing removal amount the dressing speed and resulting contact ratio Fig. 6.2 Geometry of dresser roll Table 6.7 Classication of diamond dresser rolls Natural diamond MCDaWith bonding phaseWithout bonding phase Manufacture Natural High pres- sure synthesisSintering process Gas phase deposition Hardness [Knoop]6,0 9,0,0,0 4,0,5 8,5,0 Application All dia- mond toolsStationary dressersCorner reinforcement for form rolls wear protectionForm rolls with small radii and angles aMono-cristalline diamond2 6 Manufacturing Process Dressing Ratio dThe ratio between the circumferential speeds of the dresser roll vRand the grinding wheel Sis referred to as the dressing ratio . qdvR vS6:1 Dressing can be performed as climb dressing (positive dressing ratio) or counter rotational dressing (negative dressing ratio). The dressing ratio decisively affectsthe way in which the cutting paths of the individual dressing diamonds are cong-ured and hence the effective roughness depth of the grinding wheel. The twooverlapping rotary motions means that the path curves of the individual dressingdiamonds assume quasi-cycloid shape. positive ratio results in steeper effectivepath anks, such that counter rotational dressing tends to produce lower grinding wheel roughness [ KLOC0 ], [WESS0 ]. Guide values for the dr
the resulting grinding wheel structure are dened by: the ratio between the circumferential speeds of the grinding wheel and the dresser roll (dressing ratio) the dressing removal amount the dressing speed and resulting contact ratio Fig. 6.2 Geometry of dresser roll Table 6.7 Classication of diamond dresser rolls Natural diamond MCDaWith bonding phaseWithout bonding phase Manufacture Natural High pres- sure synthesisSintering process Gas phase deposition Hardness [Knoop]6,0 9,0,0,0 4,0,5 8,5,0 Application All dia- mond toolsStationary dressersCorner reinforcement for form rolls wear protectionForm rolls with small radii and angles aMono-cristalline diamond2 6 Manufacturing Process Dressing Ratio dThe ratio between the circumferential speeds of the dresser roll vRand the grinding wheel Sis referred to as the dressing ratio . qdvR vS6:1 Dressing can be performed as climb dressing (positive dressing ratio) or counter rotational dressing (negative dressing ratio). The dressing ratio decisively affectsthe way in which the cutting paths of the individual dressing diamonds are cong-ured and hence the effective roughness depth of the grinding wheel. The twooverlapping rotary motions means that the path curves of the individual dressingdiamonds assume quasi-cycloid shape. positive ratio results in steeper effectivepath anks, such that counter rotational dressing tends to produce lower grinding wheel roughness [ KLOC0 ], [WESS0 ]. Guide values for the dr| Model Type | Bevel-helical speed reducer B3 |
|---|---|
| Gear Type | Bevel Helical Gear |
| Weight (kg) | 900.000000 |
| Ratio Range | 1 : 12.5…71 |
| Low Speed Output | Hollow shaft with shrink disk |
| Nominal Torque | 35700 Nm |
| Mounting Arrangements | Horizontal mounting position |
| Manufacturer | Flender (Australia) Pty. Ltd. |
| Country of Manufacture | San Marino |
| Data Sheet & Drawings | rdering data continued Low speed shaft LSS Oil B3DH-9-C Bevel-helical speed reducer B3 |