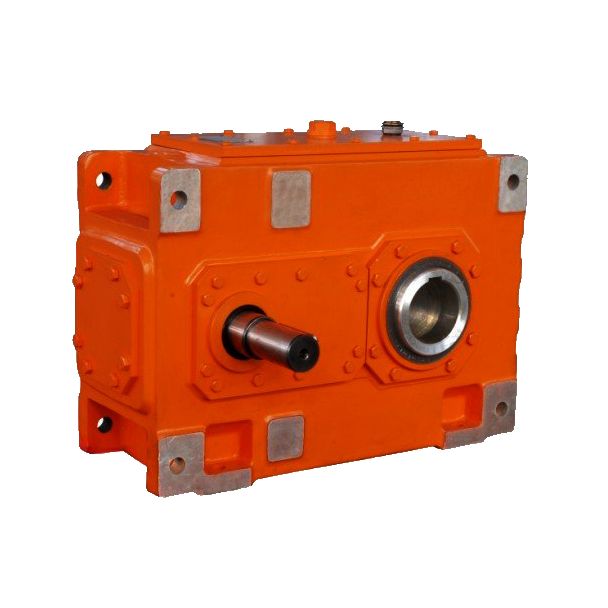
H4-CV-12B ounting position Horizontal H Vertical V Upright Helical gear Reduction Boxes H4
In stock
SKU
H4-CV-12B
$13,392.86
Flender/Flender Gear Units/Helical gear Reduction Boxes H4
has the best quality. The quality of raw material can also be tested before processing to determine the quality of the nal product. It is established that the four measurable characteristics viz., crop yield per bush ( ), hairiness of
the nal product. It is established that the four measurable characteristics viz., crop yield per bush ( ), hairiness of  leaf ( ), phloem index ( Pi), and ratio of xylem of phloem vessels on vascular bundles ( Vs)in the
leaf ( ), phloem index ( Pi), and ratio of xylem of phloem vessels on vascular bundles ( Vs)in the  following multiple regression equa- tions can predict tea avor quality and strength: Quality /H1/H1 2/H1.0 /H1.5H/H1.1 Pi/H1Vb Strength /H1/H1 2/H1.1
following multiple regression equa- tions can predict tea avor quality and strength: Quality /H1/H1 2/H1.0 /H1.5H/H1.1 Pi/H1Vb Strength /H1/H1 2/H1.1  /H1.5H/H1.0 Pi/H1Vb Phloem index is the frequency of occurrence of calcium oxalate crystals in the phloem tissue of the petiole. The estimation of TF and TR consists of extracting them into the ethyl acetate layer from the aqueous layer; further separation is achieved by shaking with sodium bicarbonatesolution. The optical densities of TF and TR are measured at 3 and 4 nm, respectively. Tannins are estimated by Lowenthals method, which is based on extraction of tan- nins into an aqueous medium and precipitation by addition of gelatin. Estimation of tanninsis carried out before and after precipitation with gelatin by titrating with standard perman-ganate solution. This step yields the oxidizable tannins present in the sample. Total caffeine is estimated by Baily-Andrews method. Caffeine is extracted into 7 Nagalakshmi aqueous medium by digesting tea leaves with heavy magnesium oxides. Then it is ex- tracted into chloroform layer and desolventized to produce caffeine in solid form. Nitro-gen is estimated in the crude caffeine by the micro-Kjeldhal method and multiplied by aconversion factor. It is reported as percentage of caffeine in the sample. The analysis ofash, water-soluble ash, alkalinity of ash, acid-insoluble ash, water extract, and crude ber uses standard procedures. Limits of specications by the Bureau of Indian Standards (percentage by mass) are total ash, 4.0%8.0%; water-soluble ash (expressed as percentage of total ash), 4.0%(minimum); acid-insoluble ash, 1.0% (maximum); alkalin
/H1.5H/H1.0 Pi/H1Vb Phloem index is the frequency of occurrence of calcium oxalate crystals in the phloem tissue of the petiole. The estimation of TF and TR consists of extracting them into the ethyl acetate layer from the aqueous layer; further separation is achieved by shaking with sodium bicarbonatesolution. The optical densities of TF and TR are measured at 3 and 4 nm, respectively. Tannins are estimated by Lowenthals method, which is based on extraction of tan- nins into an aqueous medium and precipitation by addition of gelatin. Estimation of tanninsis carried out before and after precipitation with gelatin by titrating with standard perman-ganate solution. This step yields the oxidizable tannins present in the sample. Total caffeine is estimated by Baily-Andrews method. Caffeine is extracted into 7 Nagalakshmi aqueous medium by digesting tea leaves with heavy magnesium oxides. Then it is ex- tracted into chloroform layer and desolventized to produce caffeine in solid form. Nitro-gen is estimated in the crude caffeine by the micro-Kjeldhal method and multiplied by aconversion factor. It is reported as percentage of caffeine in the sample. The analysis ofash, water-soluble ash, alkalinity of ash, acid-insoluble ash, water extract, and crude ber uses standard procedures. Limits of specications by the Bureau of Indian Standards (percentage by mass) are total ash, 4.0%8.0%; water-soluble ash (expressed as percentage of total ash), 4.0%(minimum); acid-insoluble ash, 1.0% (maximum); alkalin| Model Type | Helical gear Reduction Boxes H4 |
|---|---|
| Gear Type | Helical Gear |
| Weight (kg) | 625.000000 |
| Ratio Range | 1 : 125…450 |
| Low Speed Output | Solid shaft without parallel key |
| Nominal Torque | 78000 Nm |
| Mounting Arrangements | Vertical mounting position |
| Manufacturer | FLENDER ZAHNRADGETRIEBE |
| Country of Manufacture | Slovenia |
| Data Sheet & Drawings | H4-CV-12B ounting position Horizontal H Vertical V Upright Helical gear Reduction Boxes H4 |