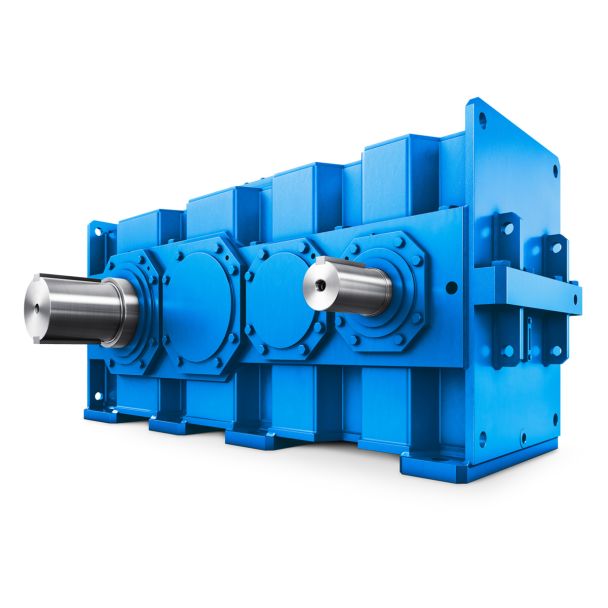
details on the shafts see Chapter Flender Gmb B3FV-27-C Bevel-helical speed reducer B3
In stock
SKU
B3FV-27-C
$488,571.43
Flender/Flender Gear Units/Bevel-helical speed reducer B3
sistance to acids and, on the basis of this behavioural pro- file, are the opposite of conventional hydrophilic zeolites. One such hydrophobic molecular sieve is dealuminated -zeolite (DAY). This zeolite has the pore structure of faujasite (, -zeolite), which is
such hydrophobic molecular sieve is dealuminated -zeolite (DAY). This zeolite has the pore structure of faujasite (, -zeolite), which is  characterised by pore diameter of approx. 0.8 nmand large micropore volume (approx. 0.3 cm3/). However, while Xand -zeolites are highly
characterised by pore diameter of approx. 0.8 nmand large micropore volume (approx. 0.3 cm3/). However, while Xand -zeolites are highly  olar adsorbents, dealuminated -zeolite displays pronounced selectivity in favour of nonpotr organic compounds. Figure 1 illustrates the different adsorption properties
olar adsorbents, dealuminated -zeolite displays pronounced selectivity in favour of nonpotr organic compounds. Figure 1 illustrates the different adsorption properties  of hydrophobic, dealuminated -zeolite and the structurally similar, but hydrophilic, Nay-zeolite on the basis of the absorption of - hexane and water. In comparison with other adsorbents, such as activated charcoals, the use of dealuminated - zeolite appears to be advantageous, particularly in the following cases: for low solvent concentrations and simultaneously high air humidity for chemically aggressive adsorbates if organic compounds have to be adsorbed which tend towards oligomerisation or polymer formation on the adsorbent: Dealuminated -zeolite is stable well above 1C and therefore, be regenerated at high temperatures. if the danger of an adsorber fire exists: Being purely inorganic material, dealuminated - zeolite is non-combustible for continuous exhaust air purification processes (.. rotor technique), when rapid adsorption and desorption is necessary. These advantages were the motivating factor behind their research project, which aimed at designing process for the manufacture of dealuminated -zeolite suitable as adsorbents for the removal and recovery of solvents from humid exhaust air. 2. Working steps Dealuminated -zeolite suitable for this application can be synthesised by reactin NaY-zeo- sary post-treatment steps were the concrete task within the project Accordingly, the working programme was split into two large blocks lite with silicon tetrachloride Development
of hydrophobic, dealuminated -zeolite and the structurally similar, but hydrophilic, Nay-zeolite on the basis of the absorption of - hexane and water. In comparison with other adsorbents, such as activated charcoals, the use of dealuminated - zeolite appears to be advantageous, particularly in the following cases: for low solvent concentrations and simultaneously high air humidity for chemically aggressive adsorbates if organic compounds have to be adsorbed which tend towards oligomerisation or polymer formation on the adsorbent: Dealuminated -zeolite is stable well above 1C and therefore, be regenerated at high temperatures. if the danger of an adsorber fire exists: Being purely inorganic material, dealuminated - zeolite is non-combustible for continuous exhaust air purification processes (.. rotor technique), when rapid adsorption and desorption is necessary. These advantages were the motivating factor behind their research project, which aimed at designing process for the manufacture of dealuminated -zeolite suitable as adsorbents for the removal and recovery of solvents from humid exhaust air. 2. Working steps Dealuminated -zeolite suitable for this application can be synthesised by reactin NaY-zeo- sary post-treatment steps were the concrete task within the project Accordingly, the working programme was split into two large blocks lite with silicon tetrachloride Development| Model Type | Bevel-helical speed reducer B3 |
|---|---|
| Gear Type | Bevel Helical Gear |
| Weight (kg) | 22800.000000 |
| Ratio Range | 1 : 20…71 |
| Low Speed Output | Flanged shaft |
| Nominal Torque | 1230000 Nm |
| Mounting Arrangements | Vertical mounting position |
| Manufacturer | Flender France S.A.R.L. |
| Country of Manufacture | China |
| Data Sheet & Drawings | details on the shafts see Chapter Flender Gmb B3FV-27-C Bevel-helical speed reducer B3 |