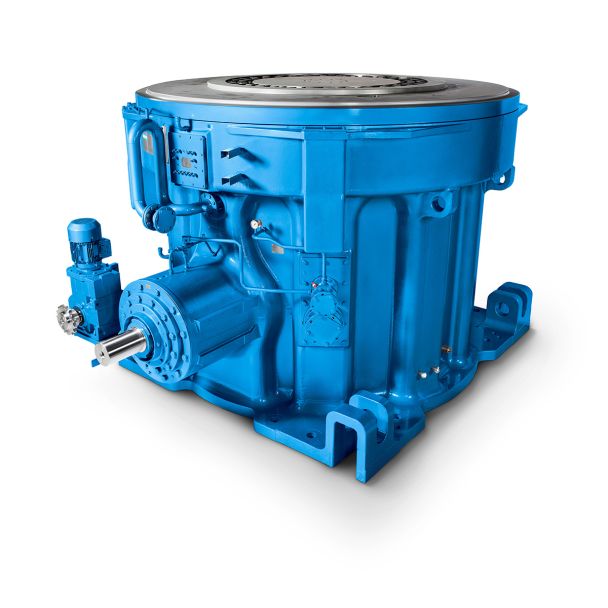
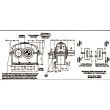
Bevel-helical gear Reduction Box B4 cial seal order via order code YSide Taconite F B4HV-14-C
In stock
SKU
B4HV-14-C
$58,607.14
Flender/Flender Gear Units/Bevel-helical gear Reduction Box B4
tored material owing to increase in moisture content and temperature uctuations can cause the development of high pressures. In general, the factors that affect the pressure distribution are moisture content of the stored material, particle size gradation, angularity of particles
the factors that affect the pressure distribution are moisture content of the stored material, particle size gradation, angularity of particles  of the stored material,temperature of the material, rate of lling, amount of aeration during lling, aeration during withdrawal, and so
of the stored material,temperature of the material, rate of lling, amount of aeration during lling, aeration during withdrawal, and so  on. Different theories are in vogue for the determination of pressure distribution on the walls. The horizontal pressures exerted by
on. Different theories are in vogue for the determination of pressure distribution on the walls. The horizontal pressures exerted by  the material on the walls are calculated usingJanssens theory, Airys theory, or Coulombs theory. In this Handbook , Janssens theory Fig. 7 Variation of Cwith /z0. Structural Considerations: Warehouse and Silo 2 Table 2 Values of Pressure Ratio ( ) and Angle of Wall Friction ( ) of Different Material Angle wall friction ( ) Pressure ratio ( ) during during Filling Emptying Sl. No Material Filling ( Kf) Emptying ( Ke)()( ) 1 Granular material /H1.2 mm 0.5 1.0 0.7 0.6 2 Powdery material /H1.0 mm 0.5 0.7 1.0 1.0 is considered for the calculations of pressure. The variation of vertical and horizontal pressure may be represented as pi()/H1pi(max)[1 /H1e/H1h/z0] pi()/H1pi(max) Where pi() is the pressure at any height handpi(max) is the maximum pressure developed in the wall; z0/H1R/();/H1[1/H1e/H1h/z0];Ris parameter known as hydraulic mean radius and is obtained by dividing the plan area ( ) of the silo by the plan perimeter ( ); is the coefcient of wall friction. The variation of parameter Cwith /z0is as shown in Fig. 7. Kis the pressure ratio, which generally lies between (1 /H1sin)/(1/H1sin) and (1/H1sin)/(1/H1sin). However, the exact value of Kis obtained experimentally. The acceptable values of in different codes for broadly classied material according to the particle size ( ) are as indicated in Table 2 (. Values of the maximum pressures ( pv,ph,pw) during lling and emptying conditions are obtained in terms of unit weight,
the material on the walls are calculated usingJanssens theory, Airys theory, or Coulombs theory. In this Handbook , Janssens theory Fig. 7 Variation of Cwith /z0. Structural Considerations: Warehouse and Silo 2 Table 2 Values of Pressure Ratio ( ) and Angle of Wall Friction ( ) of Different Material Angle wall friction ( ) Pressure ratio ( ) during during Filling Emptying Sl. No Material Filling ( Kf) Emptying ( Ke)()( ) 1 Granular material /H1.2 mm 0.5 1.0 0.7 0.6 2 Powdery material /H1.0 mm 0.5 0.7 1.0 1.0 is considered for the calculations of pressure. The variation of vertical and horizontal pressure may be represented as pi()/H1pi(max)[1 /H1e/H1h/z0] pi()/H1pi(max) Where pi() is the pressure at any height handpi(max) is the maximum pressure developed in the wall; z0/H1R/();/H1[1/H1e/H1h/z0];Ris parameter known as hydraulic mean radius and is obtained by dividing the plan area ( ) of the silo by the plan perimeter ( ); is the coefcient of wall friction. The variation of parameter Cwith /z0is as shown in Fig. 7. Kis the pressure ratio, which generally lies between (1 /H1sin)/(1/H1sin) and (1/H1sin)/(1/H1sin). However, the exact value of Kis obtained experimentally. The acceptable values of in different codes for broadly classied material according to the particle size ( ) are as indicated in Table 2 (. Values of the maximum pressures ( pv,ph,pw) during lling and emptying conditions are obtained in terms of unit weight,| Model Type | Bevel-helical gear Reduction Box B4 |
|---|---|
| Gear Type | Bevel Helical Gear |
| Weight (kg) | 2735.000000 |
| Ratio Range | 1 : 100…400 |
| Low Speed Output | Hollow shaft with keyway acc. to DIN 6885/1 |
| Nominal Torque | 113000 Nm |
| Mounting Arrangements | Vertical mounting position |
| Manufacturer | Flender Himmel RSA |
| Country of Manufacture | Panama |
| Data Sheet & Drawings | Bevel-helical gear Reduction Box B4 cial seal order via order code YSide Taconite F B4HV-14-C |