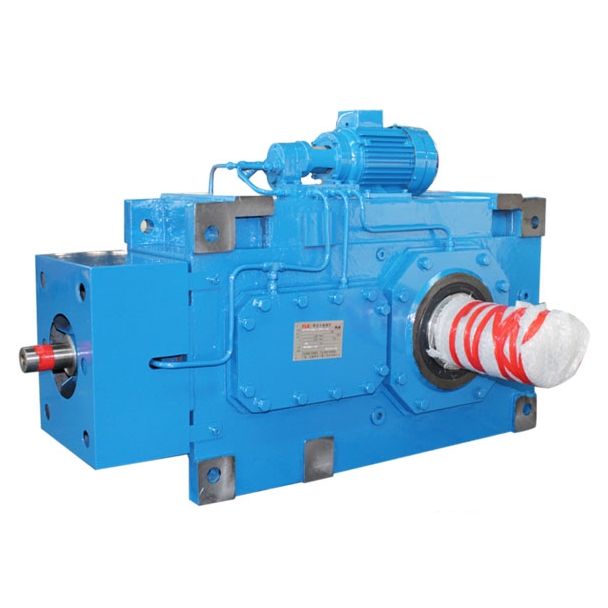
Bevel-helical gear box B4 y also be changed in the system by our service pe B4FH-19-C
In stock
SKU
B4FH-19-C
$145,714.29
Flender/Flender Gear Units/Bevel-helical gear box B4
with gamma rays from an isotope source such as 6Co is similar to the cost of irradiating with electrons from an accelerator such as 1-MeV linear accelerator. Both the gamma ray apparatus and electron accelerators are costly. The cost of
an accelerator such as 1-MeV linear accelerator. Both the gamma ray apparatus and electron accelerators are costly. The cost of  irradiating various foods has been estimated at between .. $0.0 and .. $0.4 per kilogram (WHO, . According to Mills
irradiating various foods has been estimated at between .. $0.0 and .. $0.4 per kilogram (WHO, . According to Mills  (, study carried outby Fundacion Chili in 1 demonstrated that the cost of the irradiation treatment forfruit disinfestation would be
(, study carried outby Fundacion Chili in 1 demonstrated that the cost of the irradiation treatment forfruit disinfestation would be  $0.0 per kilogram on $1 million capital investment in acobalt 6 batch-type irradiator. Kunstadt and Steeves ( discussed the economics of food irradiation application and the effects of various parameters on the cost of the treat- ment or of unit processing. They presented detailed analysis of the costs for differentstypes of cobalt 6 irradiators designed for fruit disinfestation. number of calculationswere performed for variety of doses, packing densities, and mass of production. Unitprocessing cost decreases rapidly with the increase of throughputs. Costs stabilize oncethe minimal economic throughput is reached and surpassed. Thus, successful irradiator operates at level exceeding the minimal economic mass of production. The effect of increasing the dose on unit processing costs is linear. As the dose is increased, the unitprocessing cost is also increased. It is dependent only on processing time. The effect ofdensities is also linear and related to the irradiators cobalt utilization efciency. As densityis lowered, the cost increases. Similar costs were derived for different types of cobalt 6irradiators. According to this design (.., 6-Mkg/year, 0.1 kGy, and 0.4 gcm , unit processing costs vary from below $0.0/kg or 2 Mkg/year to $0.1/kg or 1 Mkg/ year. It has to be pointed out that the calculated cost of the irradiation treatment is often offset by the increased market price differential because produce that was not previouslyaccessible is marketed, with the result that
$0.0 per kilogram on $1 million capital investment in acobalt 6 batch-type irradiator. Kunstadt and Steeves ( discussed the economics of food irradiation application and the effects of various parameters on the cost of the treat- ment or of unit processing. They presented detailed analysis of the costs for differentstypes of cobalt 6 irradiators designed for fruit disinfestation. number of calculationswere performed for variety of doses, packing densities, and mass of production. Unitprocessing cost decreases rapidly with the increase of throughputs. Costs stabilize oncethe minimal economic throughput is reached and surpassed. Thus, successful irradiator operates at level exceeding the minimal economic mass of production. The effect of increasing the dose on unit processing costs is linear. As the dose is increased, the unitprocessing cost is also increased. It is dependent only on processing time. The effect ofdensities is also linear and related to the irradiators cobalt utilization efciency. As densityis lowered, the cost increases. Similar costs were derived for different types of cobalt 6irradiators. According to this design (.., 6-Mkg/year, 0.1 kGy, and 0.4 gcm , unit processing costs vary from below $0.0/kg or 2 Mkg/year to $0.1/kg or 1 Mkg/ year. It has to be pointed out that the calculated cost of the irradiation treatment is often offset by the increased market price differential because produce that was not previouslyaccessible is marketed, with the result that| Model Type | Bevel-helical gear box B4 |
|---|---|
| Gear Type | Bevel Helical Gear |
| Weight (kg) | 6800.000000 |
| Ratio Range | 1 : 80…315 |
| Low Speed Output | Flanged shaft |
| Nominal Torque | 300000 Nm |
| Mounting Arrangements | Horizontal mounting position |
| Manufacturer | Siemens Industriegetriebe GmbH |
| Country of Manufacture | Poland |
| Data Sheet & Drawings | Bevel-helical gear box B4 y also be changed in the system by our service pe B4FH-19-C |