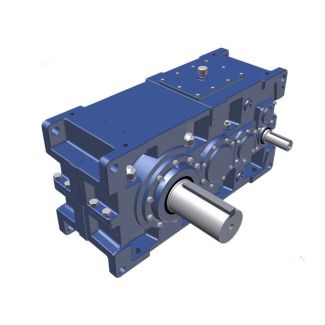
H4-DH23-B m High speed n Slow speed n Oil data oil grade o Helical gear Reduction Boxes H4
In stock
SKU
H4-DH23-B
$195,000.00
Flender/Flender Gear Units/Helical gear Reduction Boxes H4
In 1, face hobbing machine with cutter head for the continuous indexing method was developed for the rst time in Switzerland. Tooth depth was constant and the tooth lengthwise shape was an elongated epicycloid. Since then, on the one hand,
Switzerland. Tooth depth was constant and the tooth lengthwise shape was an elongated epicycloid. Since then, on the one hand,  machines with one-part tool spindle were developed, on which lengthwise crowning is generated either by means of specialcutter designs or
machines with one-part tool spindle were developed, on which lengthwise crowning is generated either by means of specialcutter designs or  by tilting the tool axis (see Sect. 2.. On the other hand, machines with two-part tool spindle for two-part cutter
by tilting the tool axis (see Sect. 2.. On the other hand, machines with two-part tool spindle for two-part cutter  heads were also developed. On thesemachines one spindle centre could be offset relative to the other, allowing anappropriate difference in tool radii for lengthwise crowning. One of these manufacturing methods is termed Zyklo-Palloid and was introduced in 1 (see Sect. 2.. The other is known under the name of Kurvex. The rst stick blade cutter heads for high volume production were introduced in 1 (see Fig. 6..6.2 Cutting of Spiral Bevel Gears 2 For decades, all these gear cutting machines had extremely complex mechanics and mechanical drive chains. Since the middle of the 1s, it has been possible toreplace these high-precision drive chains by numerically controlled drives, known as electronic gearboxes. Later, coordinate transformation was used to convert the up to ten setup- and motion-axes of the mechanical machines into the kinematics of aCNC machine with six axes. Generally speaking, all six axes move simultaneouslyin timed relationship when cutting spiral bevel gears (see Sect. 3.2.2 ). For the manufacturing methods explained in Sect. 2.1, there were originally numerous machines working on different mechanical principles, depending onwhich motions were required. Specic manufacturing methods consequentlybecame assigned to specic machine manufacturers. Progress in CNC technology made these specialized machines obsolete. Nowadays only six-axes-machines are produced which, given suitable tools, can perform nearly all known manufacturing methods for spiral bevel gears. 6.
heads were also developed. On thesemachines one spindle centre could be offset relative to the other, allowing anappropriate difference in tool radii for lengthwise crowning. One of these manufacturing methods is termed Zyklo-Palloid and was introduced in 1 (see Sect. 2.. The other is known under the name of Kurvex. The rst stick blade cutter heads for high volume production were introduced in 1 (see Fig. 6..6.2 Cutting of Spiral Bevel Gears 2 For decades, all these gear cutting machines had extremely complex mechanics and mechanical drive chains. Since the middle of the 1s, it has been possible toreplace these high-precision drive chains by numerically controlled drives, known as electronic gearboxes. Later, coordinate transformation was used to convert the up to ten setup- and motion-axes of the mechanical machines into the kinematics of aCNC machine with six axes. Generally speaking, all six axes move simultaneouslyin timed relationship when cutting spiral bevel gears (see Sect. 3.2.2 ). For the manufacturing methods explained in Sect. 2.1, there were originally numerous machines working on different mechanical principles, depending onwhich motions were required. Specic manufacturing methods consequentlybecame assigned to specic machine manufacturers. Progress in CNC technology made these specialized machines obsolete. Nowadays only six-axes-machines are produced which, given suitable tools, can perform nearly all known manufacturing methods for spiral bevel gears. 6.| Model Type | Helical gear Reduction Boxes H4 |
|---|---|
| Gear Type | Helical Gear |
| Weight (kg) | 9100.000000 |
| Ratio Range | 1 : 100…355 |
| Low Speed Output | Hollow shaft with shrink disk |
| Nominal Torque | 640000 Nm |
| Mounting Arrangements | Horizontal mounting position |
| Manufacturer | Flender Singapore Pte. Ltd. |
| Country of Manufacture | Panama |
| Data Sheet & Drawings | H4-DH23-B m High speed n Slow speed n Oil data oil grade o Helical gear Reduction Boxes H4 |