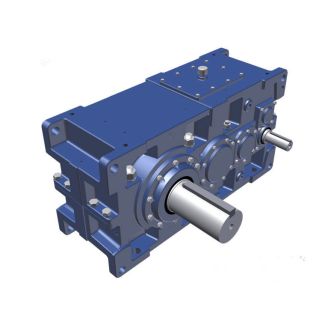
H3-VV-9-D flender corporation Helical gear Reduction Boxes H3
In stock
SKU
H3-VV-9-D
$18,750.00
Flender/Flender Gear Units/Helical gear Reduction Boxes H3
country was Java and Sumatra as substitute for coffee destroyed by coffee leaf rust. On Java, the Criollo was grown in signicant amounts in the 1s when the production of Forastero cocoa in East Java reached 5 tons. In Indonesia,
in signicant amounts in the 1s when the production of Forastero cocoa in East Java reached 5 tons. In Indonesia,  major cocoa plantations can be found in West Java, East Java, Bali, Sulawesi, and North Sumatra. The average yield per
major cocoa plantations can be found in West Java, East Java, Bali, Sulawesi, and North Sumatra. The average yield per  hectare is estimated to be between 1.7 and 2.1 tons. Cocoa in Indonesia can be harvested almost all year, except
hectare is estimated to be between 1.7 and 2.1 tons. Cocoa in Indonesia can be harvested almost all year, except  the months of August and September. The total export between January and September 1 wasabout 1,0 tons, worth .. $1 million. Table 1 shows the main producers of cocoain the Asia and Oceania region. 2 POSTHARVEST ACTIVITIES Postharvest activities commonly practiced in cocoa producing countries are shown in Fig. 1 and will be described in the following sections. These include () harvesting, () curing/fementation, () drying, () sorting and quality determination, and () packaging. 2.1 Harvesting There are three types of cocoa tree that are widely grown: the Criollo , Forastero , and theTrinitario . The basic differences among these trees are shown in Table 2. Cacao pods have several variations in form, length, hardness of the skin, and color. The forms can be spherical to cylindrical, while the skin may have spikes and holes. Thefollowing are common forms of cocoa pods (Spillane, : 1.Angoleta : deeply ridged, warty, with square form at the stalk end 2.Cundeamor : more or less the same as Angoleta , but the neck resembles bottle 3.Amelonado : smooth, shallow furrows; resembles melon with one end blunt; resembles bottle 4.Calabacillo : small and spherical Harvest time of mature cocoa varies from place to place from 1 days after owering in Nigeria to 1 days after owering in Papua New Guinea. Accordingto Alvim et al. ( maturity can be estimated using the following empirical formula: /H1/( /H ( Cocoa 7Table 1 Production of Cocoa from the Asian and Oceania Region in Thousands of Tons 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Count
the months of August and September. The total export between January and September 1 wasabout 1,0 tons, worth .. $1 million. Table 1 shows the main producers of cocoain the Asia and Oceania region. 2 POSTHARVEST ACTIVITIES Postharvest activities commonly practiced in cocoa producing countries are shown in Fig. 1 and will be described in the following sections. These include () harvesting, () curing/fementation, () drying, () sorting and quality determination, and () packaging. 2.1 Harvesting There are three types of cocoa tree that are widely grown: the Criollo , Forastero , and theTrinitario . The basic differences among these trees are shown in Table 2. Cacao pods have several variations in form, length, hardness of the skin, and color. The forms can be spherical to cylindrical, while the skin may have spikes and holes. Thefollowing are common forms of cocoa pods (Spillane, : 1.Angoleta : deeply ridged, warty, with square form at the stalk end 2.Cundeamor : more or less the same as Angoleta , but the neck resembles bottle 3.Amelonado : smooth, shallow furrows; resembles melon with one end blunt; resembles bottle 4.Calabacillo : small and spherical Harvest time of mature cocoa varies from place to place from 1 days after owering in Nigeria to 1 days after owering in Papua New Guinea. Accordingto Alvim et al. ( maturity can be estimated using the following empirical formula: /H1/( /H ( Cocoa 7Table 1 Production of Cocoa from the Asian and Oceania Region in Thousands of Tons 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Count| Model Type | Helical gear Reduction Boxes H3 |
|---|---|
| Gear Type | Helical Gear |
| Weight (kg) | 875.000000 |
| Ratio Range | 1 : 25…90 |
| Low Speed Output | Solid shaft with parallel key acc. to DIN 6885/1 with reinforced spigot |
| Nominal Torque | 35700 Nm |
| Mounting Arrangements | Vertical mounting position |
| Manufacturer | Flender France S.A.R.L. |
| Country of Manufacture | Romania |
| Data Sheet & Drawings | H3-VV-9-D flender corporation Helical gear Reduction Boxes H3 |