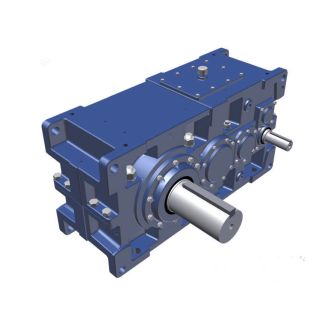
Bevel-helical gearboxes B4 ion with oil circulation lubrication Radial shaf B4-HV-22-A
In stock
SKU
B4-HV-22-A
$212,142.86
Flender/Flender Gear Units/Bevel-helical gearboxes B4
treatment methods with potential for valuahe material recovery, such as separation or the membrane separation methods. For example, even deter ents rated as being ,,very readily ultrafilterable" by their manufacturers lost this property afterteing used for essential components. Thus, the
ents rated as being ,,very readily ultrafilterable" by their manufacturers lost this property afterteing used for essential components. Thus, the  primary task of further development is to optimise the detergent/lubricoolant systems with respect to lower stability in conjunction with maintenance
primary task of further development is to optimise the detergent/lubricoolant systems with respect to lower stability in conjunction with maintenance  of the cleaning effect. 2 Duration: 0 0- 3 0 0 ZH8 1 2 Subject: Reduction of halogenated hydrocarbon emissions
of the cleaning effect. 2 Duration: 0 0- 3 0 0 ZH8 1 2 Subject: Reduction of halogenated hydrocarbon emissions  - Sub-Project. Reduction of the environmental burden caused surface cleaning by substituting chlorinated hydrocarbons wit[ aqueous systems Research centre: Karl Walter Reinigungsmittelwerk GmbH Werner-von-Siemensdtrasse 1 2,2 Kaltenkirchen Government sponsorship: DM 6 3.1 2 9 Sponsorship ratio: 5% 1. Purpose of the project Chlorinated hydrocarbons (CHCs) constitute considerable potential danger to man and the Environment. Although the production figures in the Federal Republicof Germany (old Lander) show downward trend, the quantities used are still significant potential risk. Tetrachloroethylene and 1 , , -trichloroethane have primarily been used up to now for indus- trial metal degreasing. The main goal of this project is to develop ueous cleaning systems which can significantly reduce the current quantities of CHCs use% and are alternatives to CHCs, which are danger to health and to water supplies (Water Hazard Class . The metal-working industry places widely differin demands on such cleaning and degreasing systems. This is due to the large number of metaSfic materials in the most diverse processing states. In addition, thereare innumerableauxiliary metalworking agents which must be remov- ed from the metal surfaces together with chips, dust, etc. Thus, the chemical research goal is to develop aqueous substitution products for CHCs. This ,oal is given priority over degreasers on an organ
- Sub-Project. Reduction of the environmental burden caused surface cleaning by substituting chlorinated hydrocarbons wit[ aqueous systems Research centre: Karl Walter Reinigungsmittelwerk GmbH Werner-von-Siemensdtrasse 1 2,2 Kaltenkirchen Government sponsorship: DM 6 3.1 2 9 Sponsorship ratio: 5% 1. Purpose of the project Chlorinated hydrocarbons (CHCs) constitute considerable potential danger to man and the Environment. Although the production figures in the Federal Republicof Germany (old Lander) show downward trend, the quantities used are still significant potential risk. Tetrachloroethylene and 1 , , -trichloroethane have primarily been used up to now for indus- trial metal degreasing. The main goal of this project is to develop ueous cleaning systems which can significantly reduce the current quantities of CHCs use% and are alternatives to CHCs, which are danger to health and to water supplies (Water Hazard Class . The metal-working industry places widely differin demands on such cleaning and degreasing systems. This is due to the large number of metaSfic materials in the most diverse processing states. In addition, thereare innumerableauxiliary metalworking agents which must be remov- ed from the metal surfaces together with chips, dust, etc. Thus, the chemical research goal is to develop aqueous substitution products for CHCs. This ,oal is given priority over degreasers on an organ| Model Type | Bevel-helical gearboxes B4 |
|---|---|
| Gear Type | Bevel Helical Gear |
| Weight (kg) | 9900.000000 |
| Ratio Range | 1 : 90…355 |
| Low Speed Output | Hollow shaft with keyway acc. to DIN 6885/1 |
| Nominal Torque | 470000 Nm |
| Mounting Arrangements | Vertical mounting position |
| Manufacturer | Flender (Australia) Pty. Ltd. |
| Country of Manufacture | Tajikistan |
| Data Sheet & Drawings | Bevel-helical gearboxes B4 ion with oil circulation lubrication Radial shaf B4-HV-22-A |